Hanover Hound

Description
The Hanover Hound, also known as the Hannoverian Scenthound, is a breed of dog originally developed in Germany for hunting purposes, particularly for tracking and trailing game. The breed is known for its excellent scenting abilities and tireless work ethic, making it a prized companion for hunters, especially in the pursuit of large game like boar, deer, and wild cats. The Hanover Hound's origins date back to the 19th century, when it was bred by crossing local German hounds with other breeds to create a dog with a powerful nose, stamina, and a strong desire to track scent over long distances.
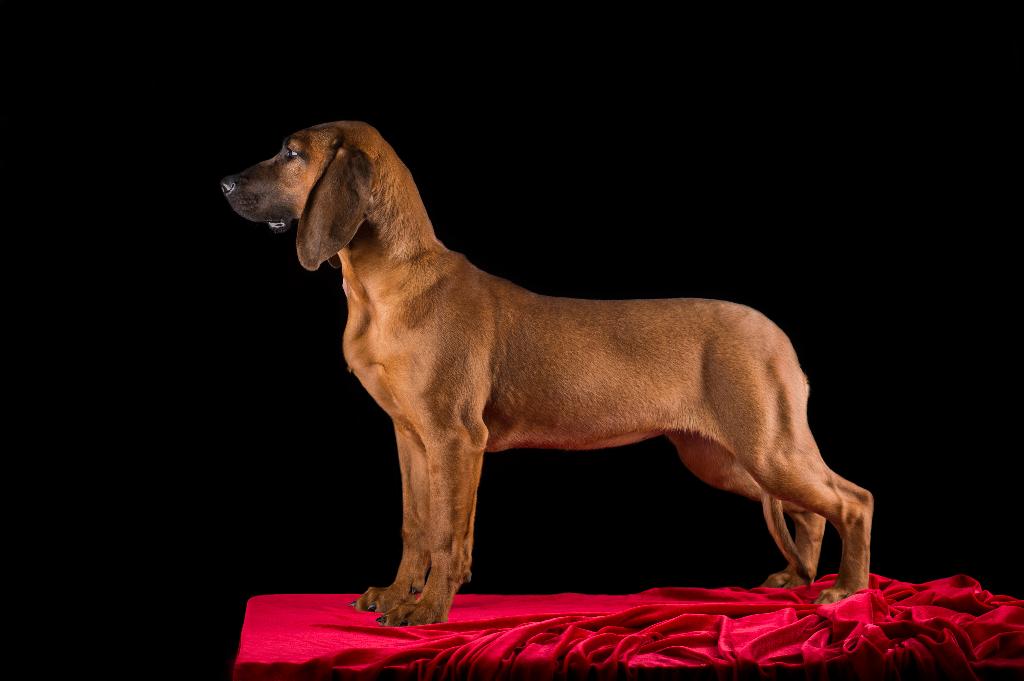
Physically, the Hanover Hound is a medium to large dog, characterized by its strong, muscular build and distinctive coat. The breed has a short, dense, and weather-resistant coat that is typically a reddish-brown or tan color, sometimes with darker markings. The Hanover Hound’s face is expressive, with long, drooping ears and dark, intelligent eyes. The breed’s legs are well-muscled, built for endurance, and its tail is often carried in a slight curve, which gives it a dignified appearance. Despite its robust build, the Hanover Hound maintains a level of agility that is essential for its role as a working hunting dog.
Hanover Hounds are known for their exceptional scenting ability and perseverance when it comes to tracking. Once they pick up a scent, they follow it with unwavering determination, making them invaluable for hunters needing a reliable tracking dog. The breed is often used in Germany and other parts of Europe for hunting and is particularly valued for its ability to track wounded game over long distances. Hanover Hounds are highly intelligent, and their strong independent streak means they can sometimes be a challenge to train. However, they respond well to consistent training, particularly when they are given tasks that engage their natural hunting instincts.
While they are primarily working dogs, Hanover Hounds can also make loyal pets for the right owners. They are affectionate and gentle, particularly with their families, but their strong hunting drive means they require proper training and socialization. As active dogs, they need plenty of exercise and mental stimulation. Without sufficient activity, they can become bored and potentially destructive. Hanover Hounds thrive in homes with large, secure yards where they can get regular outdoor time, and they are happiest when given the opportunity to perform tasks that engage their scenting abilities, such as tracking or obedience training.
In conclusion, the Hanover Hound is a hardworking, intelligent, and dedicated breed that excels in scent work and tracking. With its strong hunting background, this breed requires an active and experienced owner who can provide both physical exercise and mental stimulation. While they are best suited for those who engage in hunting or other scent-driven activities, Hanover Hounds can also make affectionate and loyal companions in the right environment. Their combination of stamina, intelligence, and loyalty makes them a versatile and reliable dog for both working and family life.
History
The Hanover Hound, or *Hannoverscher Schweißhund*, is a specialized scent hound with a history that dates back to medieval Germany. The breed was developed for its exceptional ability to track wounded game, a practice known as blood tracking (*Schweißarbeit*). Its origins lie in the large, heavy hounds used by German nobles and gamekeepers during the Middle Ages, particularly the "Liam Hounds" (*Leithunde*), which were bred to follow the scent trails of injured animals. These dogs were critical for retrieving game in dense forests, ensuring ethical hunting practices and minimizing the suffering of wounded animals.
In the 17th century, the Hanoverian hunting tradition flourished, and the Hanover Hound emerged as a distinct breed in the region of Hanover, northern Germany. Breeders focused on refining the dog’s scenting ability, stamina, and loyalty, traits that were essential for tracking game over long distances. The breed’s methodical and determined approach to tracking made it invaluable to hunters. Unlike other hounds that pursued game actively, the Hanover Hound specialized in following the faint scent trails left by wounded animals, often over challenging terrain and long periods.
The Hanover Hound was formally standardized in the 19th century when the breed’s traits were documented and preserved by the Hanoverian hunting estates. In 1894, the first breed club, the Verein Hirschmann, was established to promote and protect the breed. Despite its specialized skills, the Hanover Hound faced declining numbers in the 20th century due to changes in hunting practices and the reduced need for blood tracking. However, dedicated breeders and enthusiasts have ensured the breed’s survival, maintaining its role as a reliable working dog.
Today, the Hanover Hound remains a highly regarded breed among hunters, particularly in Europe, where ethical hunting and game management continue to value its tracking abilities. While it is less common as a companion dog due to its working nature, the breed is admired for its intelligence, loyalty, and calm temperament. Its rich history reflects its enduring importance as a specialized hunting partner and a symbol of Germany’s hunting heritage.
Colors
• Brindle
• Fawn
• Red